Interaction design is the definition of digital behavior, from desktop software and mobile applications to components of appliances, automobiles, and even biomedical devices. Where architects plan buildings, graphic designers make visual compositions, and industrial designers give form to three-dimensional objects, interaction designers define the digital components of products and services. These include websites, mobile applications, desktop software, automobiles, consumer electronics, and more. Interaction design is a relatively new but fast-growing discipline, emerging with the explosive growth of the World Wide Web. In a software-saturated world, every day, multiple times a day, billions of people encounter the work products of interaction design.
Given the reach of their profession, how interaction designers work is of paramount concern. In considering interaction design, this dissertation turns away from a longstanding question of design studies: How does interaction design demonstrate a special form of human thought? And towards a set of questions drawn from practice-oriented studies of science and technology: What kinds of objects and subjects do interaction design practices make, and how do those practices produce them?
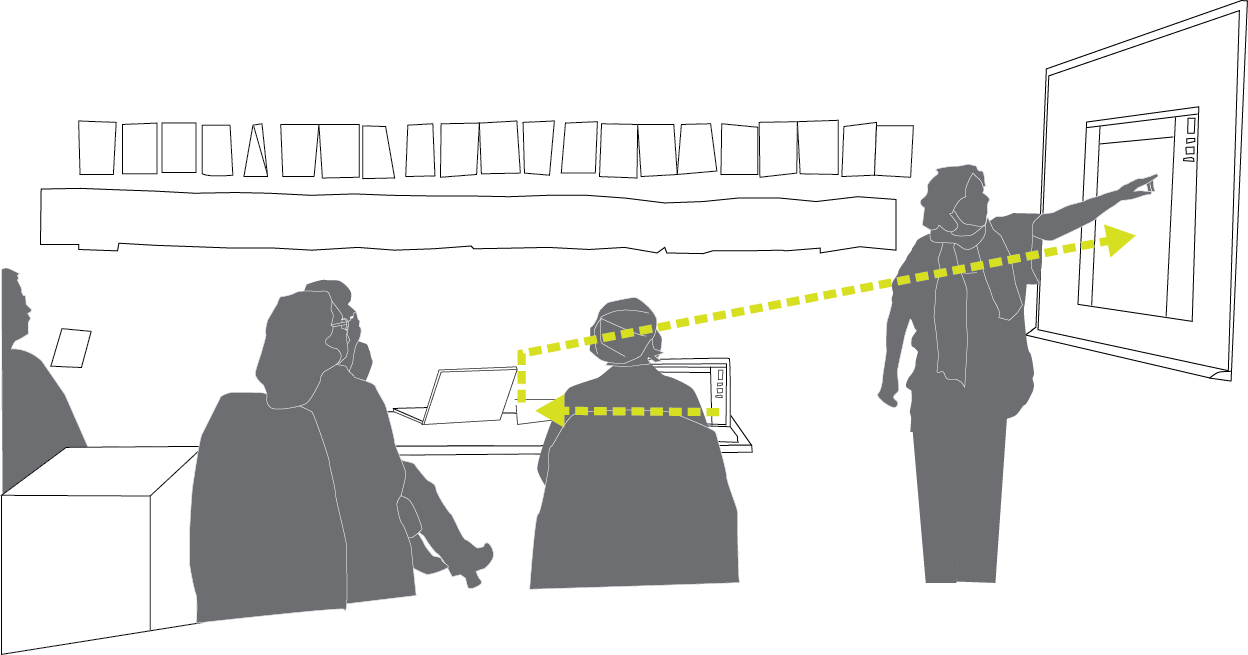
Based on participant observation at three San Francisco interaction design consultancies and interviews with designers in California’s Bay Area, this dissertation argues that performance practices organize interaction design work. By “performance practices,” I mean episodes of storytelling and narrative that take place before an audience of witnesses. These performances instantiate — make visible and tangibly felt — the human and machine behaviors that the static deliverables seem unable on their own to materialize. In doing so, performances of the project help produce and sustain alignment within teams and among designers, clients, and developers.
In this way, a focus on episodes of performance turns our concerns from cognition, in which artifacts assist design thinking, to one of enactment, in which documents, spaces, tools, and bodies actively participating in producing the identities, responsibilities, and capacities of project constituents. It turns our attention to questions of political representation, materiality and politics. From this perspective, it is not necessarily how designers think but how they stage and orchestrate performances of the project that makes accountable, authoritative decision-making on behalf of clients and prospective users possible.
Download PDF
 "Garden tours" of San Francisco community gardens.
"Garden tours" of San Francisco community gardens. Historical analysis of park design and politics.
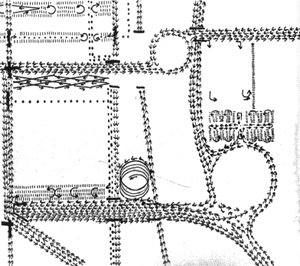
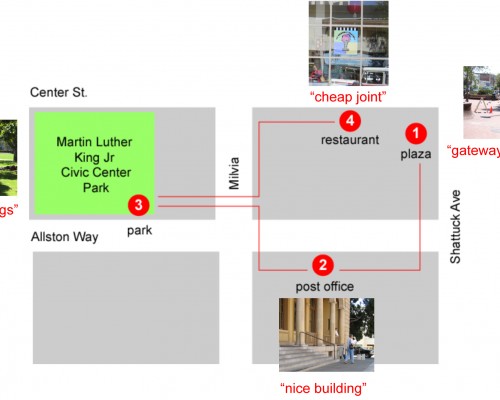
Historical analysis of park design and politics. Design concept sketches
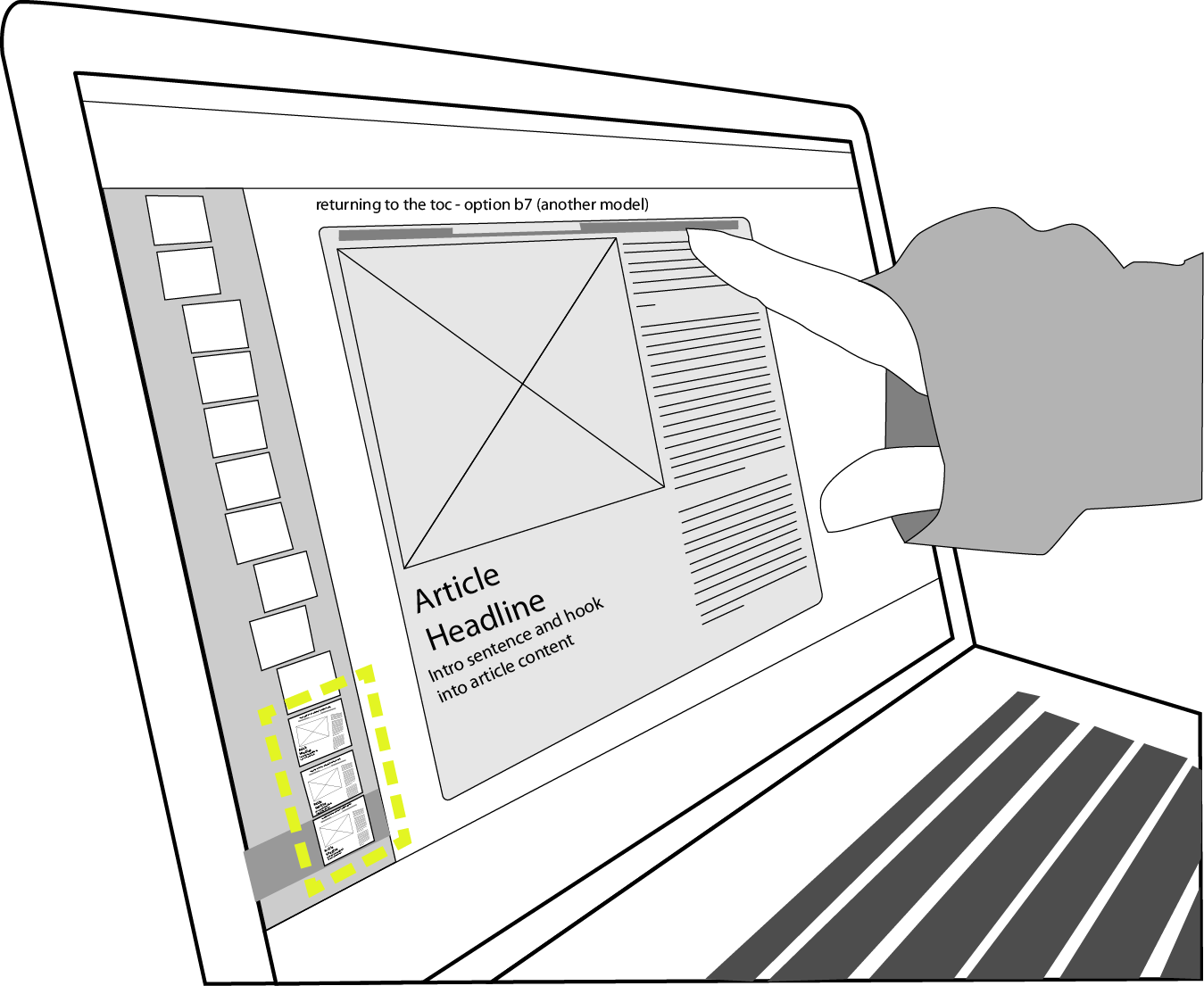
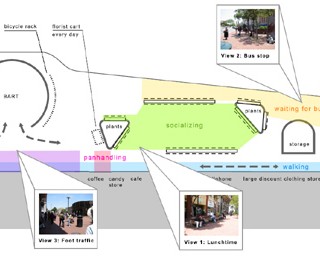
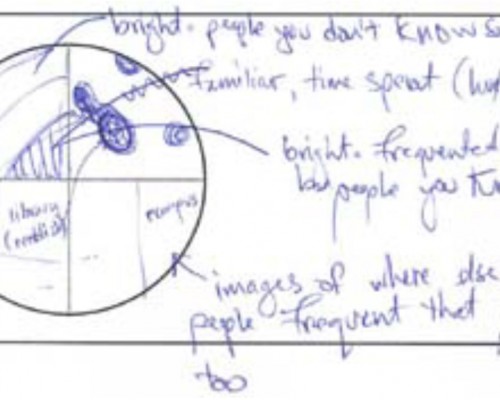
Design concept sketches
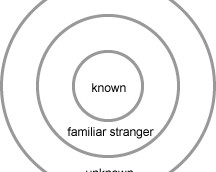
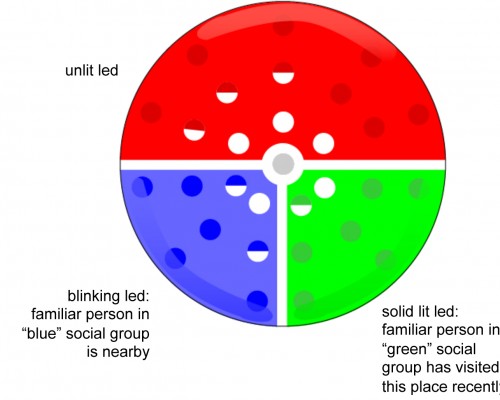
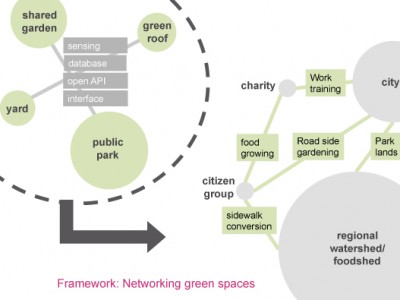 Service ecology diagrams
Service ecology diagrams